

Isotacticity of polypropylene
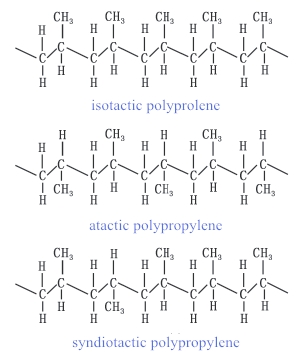
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic resin prepared by polymerization of propylene. There are three kinds of polypropylene, isotactic polypropylene, atactic polypropylene and syndiotactic polypropylene.
Isotactic polypropylene is called if the methyl groups are arranged on the same side of the main chain. Syndiotactic polypropylene is called if the methyl groups are arranged disorderly on both sides of the main chain. Atactic polypropylene is called when the methyl groups are arranged alternately on both sides of the main chain. In General Industrial Polypropylene resin, the isotactic structure content is about 95%, the rest is atactic or syndiotactic polypropylene. Industrial products are mainly composed of isotactic substances. Polypropylene also contains propylene and a small amount of ethylene copolymer. It is usually translucent and colorless solid, odorless and non-toxic. Because the structure is regular and highly crystallized, the melting point can be as high as 167 C. Heat resistance, corrosion resistance and steam sterilization are the outstanding advantages of products. The density is small, is the lightest general plastic. The disadvantage is low temperature impact resistance and easy ageing, but can be overcome by modification.
Copolymer PP has lower hot deformation temperature (100 C), low transparency, low gloss and low rigidity, but has stronger impact strength. The impact strength of PP increases with the increase of ethylene content. The softening temperature of VEKA PP is 150 C. Because of the high crystallinity, the surface stiffness and scratch resistance of the material are very good. There is no environmental stress cracking problem in PP.
The melt mass flow rate (MFR) of PP is usually 1~100. Low MFR PP materials have better impact resistance but lower ductility. For the same MFR material, the impact strength of the copolymer is higher than that of the homopolymer. Because of the crystallization, the shrinkage of PP is quite high, generally 1.6~2.0%.